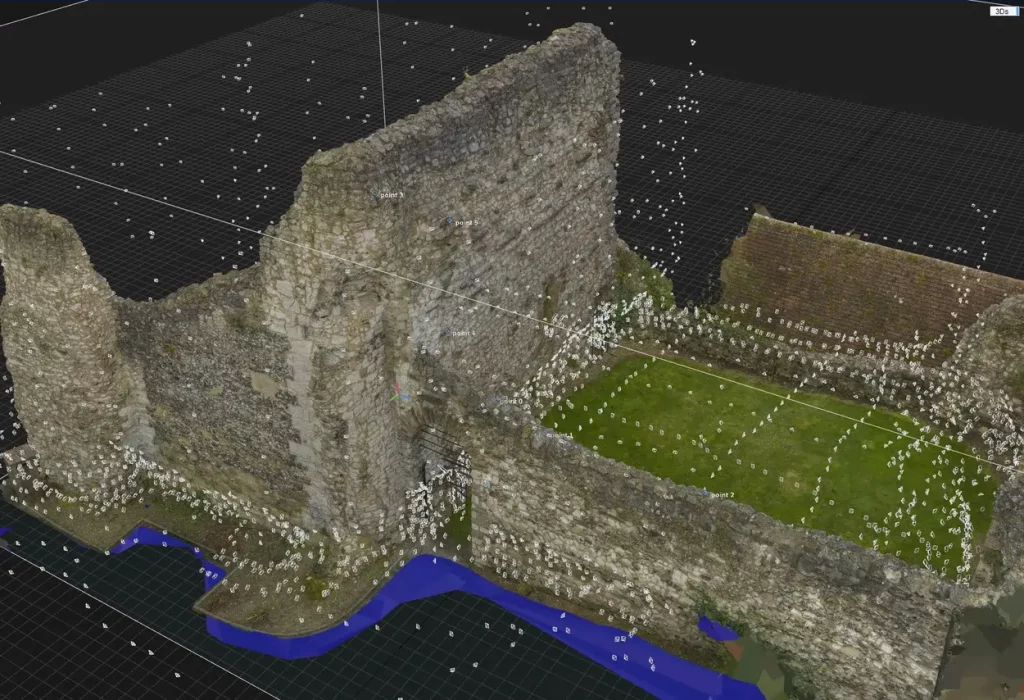
In today’s rapidly evolving world, technology has become an indispensable tool for architects and designers. From virtual reality simulations to building information modeling (BIM), these advancements have revolutionized the way professionals envision and create architectural masterpieces.
Among these advancements is the use of photogrammetry in 3D modeling for architects, which has opened many doors. With its ability to capture detailed 3D models from photographs, photogrammetry is transforming the field of home designing. Coupled with 3D visualization, this technology is making it easier for architects to provide photorealistic representations of their designs.
Understanding Photogrammetry and its Application
Photogrammetry is the technique of creating 3D models from photographs. Architects use it, combined with tools like Archicad, to gather precise details of existing structures or terrains, aiding design. While there’s a learning curve and it might get time consuming, the results are invaluable.
The advantages of using photogrammetry in home designing processes are immense. It enhances visualization, allowing clients to see lifelike 3D models of their future homes. Plus, by offering accurate early-stage data, photogrammetry ensures architects make decisions based on exact measurements, not just estimates.
Photogrammetry Workflow for Architects
The process of using photogrammetry in architectural design involves several key steps:
- Architects capture images of the site using various tools such as drones or cameras, sometimes even employing laser scanning for precise details. These high-quality images from various angles serve as the foundation for 3D modeling.
- Once the images have been captured, software programs are used to generate precise 3D models from the collected data, extracting measurements and geometry.
- During this modeling process, precision and attention to detail are crucial. This approach allows architects to achieve realistic design visualizations with true-to-life context.
Benefits of Photogrammetry in Home Designing
Photogrammetry plays an invaluable role in modern architecture by providing a range of advantages for home designers such as:
Enhancing visualization and communication with clients:
One of the key benefits of photogrammetry is its ability to enhance visualization and communication with clients. With detailed 3D models, architects can provide realistic representations of their designs, allowing clients to better understand and visualize the proposed spaces. This not only improves client satisfaction but also reduces misunderstandings during the construction phase.
Streamlining the design iteration process:
By capturing accurate data from real-world environments, architects can quickly make changes and adjustments to their designs without needing multiple site visits or lengthy measurements. This saves time and resources while still ensuring precision in every aspect of the project.
Incorporating real-world context into architectural designs:
Incorporating real-world context into architectural designs is made possible through photogrammetry. By accurately modeling existing structures or natural surroundings, architects can seamlessly integrate new designs into their surroundings. This ensures that new homes blend harmoniously with their environment and take full advantage of unique site features such as views or sunlight patterns.
Read also – 12 Best 3D Architecture Software To Create Better Designs
Applications of Photogrammetry in Different Design Phases
Architects are increasingly turning to photogrammetry for its wide range of applications throughout various design phases.
Conceptual design: Using photogrammetry to analyze site conditions
Conceptual design is the initial stage where architects brainstorm ideas and analyze site conditions. With photogrammetry, they can obtain accurate data about the terrain, topography, and surrounding structures. This information helps them make informed decisions regarding building placement, orientation, and overall design concept.
Schematic design: Incorporating accurate site data into initial plans
In the schematic design phase, architects incorporate precise site data into their initial plans. By using photogrammetric techniques to capture detailed images of existing buildings or landscapes, they can create 3D models that accurately represent real-world conditions. This allows designers to seamlessly integrate their proposed designs with the existing environment.
Design development: Fine-tuning the design with photogrammetric insights
During the design development phase, photogrammetry provides valuable insights for fine-tuning architectural designs. By analyzing captured data from various angles and perspectives, architects can identify potential issues or constraints early on. They can then make necessary adjustments to improve functionality and aesthetics before advancing further in the process.
Construction documentation: Creating detailed and context-rich blueprints
When it comes to construction documentation, photogrammetry plays a crucial role in creating detailed blueprints enriched with contextual information. By capturing high-resolution images of existing structures or landscapes on-site and converting them into 3D models, architects ensure that every detail is accounted for during the construction phase.
Read also – 9 Tips To Improve Your Architectural Visualizations
Tools and Software for Architectural Photogrammetry
When it comes to architectural photogrammetry, there are several powerful tools available that can help architects create accurate and detailed 3D models. Some of the popular tools and software for architectural photogrammetry are:
Pix4D:
Pix4D allows architects to create detailed models by stitching together aerial images captured using drones. This software offers advanced features like point cloud generation and mesh reconstruction, making it an ideal choice for architectural projects.
RealityCapture:

RealityCapture is yet another popular choice among architects for photogrammetric modeling. This versatile software supports various input formats and provides efficient meshing algorithms for generating highly-detailed models. Architects can also benefit from its automatic marker detection feature which simplifies the georeferencing process.
Agisoft Metashape:
Another widely-used tool in the field of architectural photogrammetry is Agisoft Metashape (formerly known as Photoscan). This software utilizes a technique called Structure from Motion (SfM) to reconstruct 3D models from 2D images. It also offers features such as dense point cloud generation, mesh texturing, and orthophoto production.
Case Studies: Real-World Examples of Photogrammetry in Architecture
Example 1: Revitalizing urban spaces with accurate site models
Case Study: Photogrammetry in Boulevard Façade Renovation
Objective:
To redesign and renovate building façades on the Boulevard, ensuring harmony with the existing environment.
Methodology:
- Photogrammetric Data Collection: Utilized high-resolution images from a calibrated digital camera.
- Over 250 photos were captured at different times of the day to assess the current façade conditions.
- Challenges such as vehicle traffic and pedestrian obstructions required early morning photography and additional shots for buildings obscured by trees.
- Data Processing: The images were processed using close-range photogrammetry techniques integrated with geographical information systems. This enabled detailed evaluation of the building façades.
Outcome:
Based on the processed data, recommendations were provided to reduce visual pollution, resulting in a more aesthetic and harmonious Boulevard environment.
Significance:
This project showcases how photogrammetry, even in challenging urban scenarios, can effectively aid in architectural renovation and revitalization, producing accurate site models for better urban design decisions.
Read also – Best Examples of 3D Printed Houses Around the World: Pushing the Boundaries of Modern Architecture
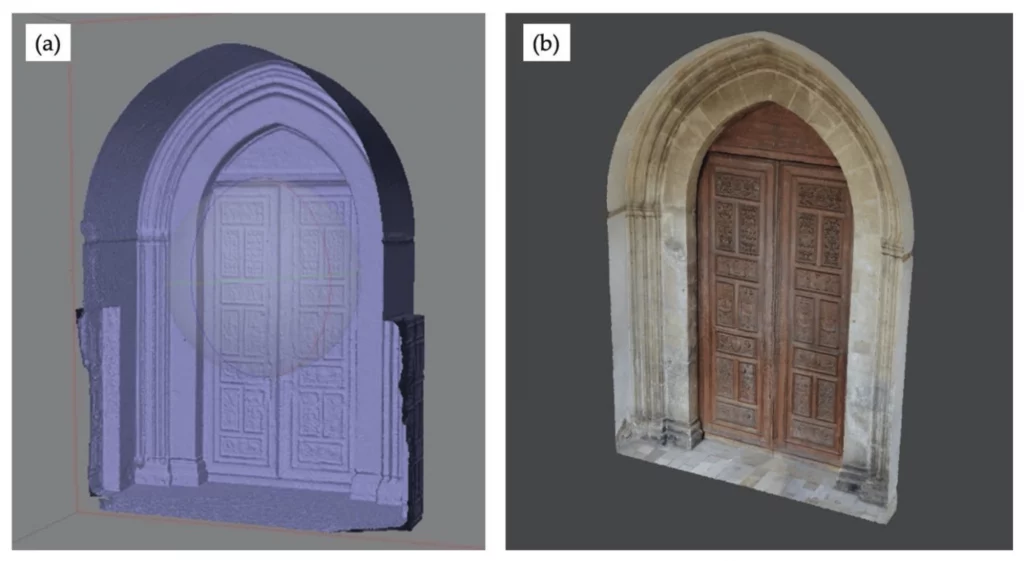
Example 2: Preservation and renovation projects driven by photogrammetry
Case Study: Preservation and Renovation of the San Domenico Church Main Entrance Portal Using Photogrammetry
The San Domenico Church in South Calabria, Italy, showcases the region’s rich architectural heritage. Over time, its entrance portal deteriorated, posing concerns about preservation.
Problem:
Assessing the intricate portal’s damage visually was challenging. Traditional methods were invasive and possibly incomplete.
Methodology:
Researchers employed photogrammetry, which uses photos for accurate measurements and 3D modeling.
- Data Collection: High-resolution cameras captured images from various angles, encompassing close-ups and broader views.
- 3D Model Generation: Specialized software produced a detailed 3D model, acting as a digital replica, enabling damage examination without physical interaction.
- Damage Assessment: Using the model, they quantified the decay, guiding restoration prioritization.
Results:
Photogrammetry offered:
- Detailed Insights: The model unveiled hidden decay areas.
- Objective Measurement: Restoration became data-driven, focusing on actual needs over subjective evaluations.
- Documentation: The digital representation offers a baseline for future assessments.
Thus, this method not only aids the San Domenico Church’s portal restoration but also suggests a pioneering approach for global cultural heritage preservation.
Read also – 3D Modeling vs 3D Rendering
Challenges and Considerations in Architectural Photogrammetry
Architectural photogrammetry has revolutionized the way architects design homes, but like any technology, it comes with its fair share of challenges:
Dealing with complex terrains and challenging lighting conditions:
One major challenge is dealing with complex terrains and challenging lighting conditions. Uneven surfaces or areas with poor lighting can pose difficulties in capturing accurate data for 3D modeling.
Ensuring data accuracy and mitigating errors in the modeling process
Ensuring data accuracy and mitigating errors also requires careful consideration. The precision and detail required in the modeling process are crucial to creating realistic representations of architectural designs. Any inaccuracies or errors can lead to flawed models that may impact the final outcome.
Addressing privacy and legal concerns related to data collection
Another important aspect when using photogrammetry is addressing privacy and legal concerns related to data collection. As architects capture images from public spaces or properties, they must navigate privacy laws and obtain proper consent if necessary.
Read also – 14 Top 3D Rendering Issues That Every Interior Designer Has To Face
The Future of Photogrammetry in Architectural Design
The future of photogrammetry in architectural design holds immense potential in revolutionizing the way homes are designed. Key advancements include:
- One emerging trend is integrating photogrammetry with other tools like VR or AR, allowing architects to offer immersive pre-built design walkthroughs.
- Another exciting development is using AI algorithms to automate photogrammetric tasks, enhancing speed and accuracy by minimizing human error.
- Furthermore, Drone technology advancements, facilitating aerial photogrammetry, providing high-resolution images and enabling precise modeling of large-scale projects are some other noticeable trends
Looking ahead, it is clear that photogrammetry will continue to play a crucial role in home designing processes. These innovations underscore photogrammetry’s growing significance in crafting homes harmoniously integrated with their environment.
Conclusion:
Photogrammetry has significantly transformed home design, enabling architects to produce more accurate and detailed designs tailored to client needs. This technology allows architects to capture real-world data with precision and turn it into 3D models, providing a vivid preview of the end result.
However, for architects to remain at the forefront, ongoing learning and adaptation are crucial. Embracing photogrammetry, they can design functional yet aesthetically pleasing spaces. So, as we merge technology with architecture, let’s celebrate by raising our cameras and drones!
FAQs
3D scanning involves using specialized hardware to capture the geometry of an object, whereas photogrammetry involves analyzing and stitching together multiple 2D images to create a 3D model.
Photogrammetry uses images for 3D reconstruction, while LiDAR employs lasers to measure distances. Their suitability varies based on accuracy needs, environmental conditions, and cost. Choosing between them depends on the specific application.
Photogrammetry helps architects create precise 3D models of spaces, enhancing design accuracy. It eliminates manual measurements, saving time and offering a detailed view of the site.
For architectural photogrammetry, you’ll need a digital camera with manual settings, a tripod, measuring tools like tapes or laser measures, and software like Agisoft Metashape or RealityCapture to convert images into 3D models.
Yes, photogrammetry can be used for both exterior and interior design projects. It allows for the creation of detailed 3D models of both the external structure and internal spaces, enabling designers to visualize and plan their projects accurately.